CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
- Promotes Muscle Relaxation
- Helps Alleviate Exercise-Related Muscle Pain
- Concentrated Blend of Traditional Botanicals to Soothe Muscle Tension
OVERVIEW
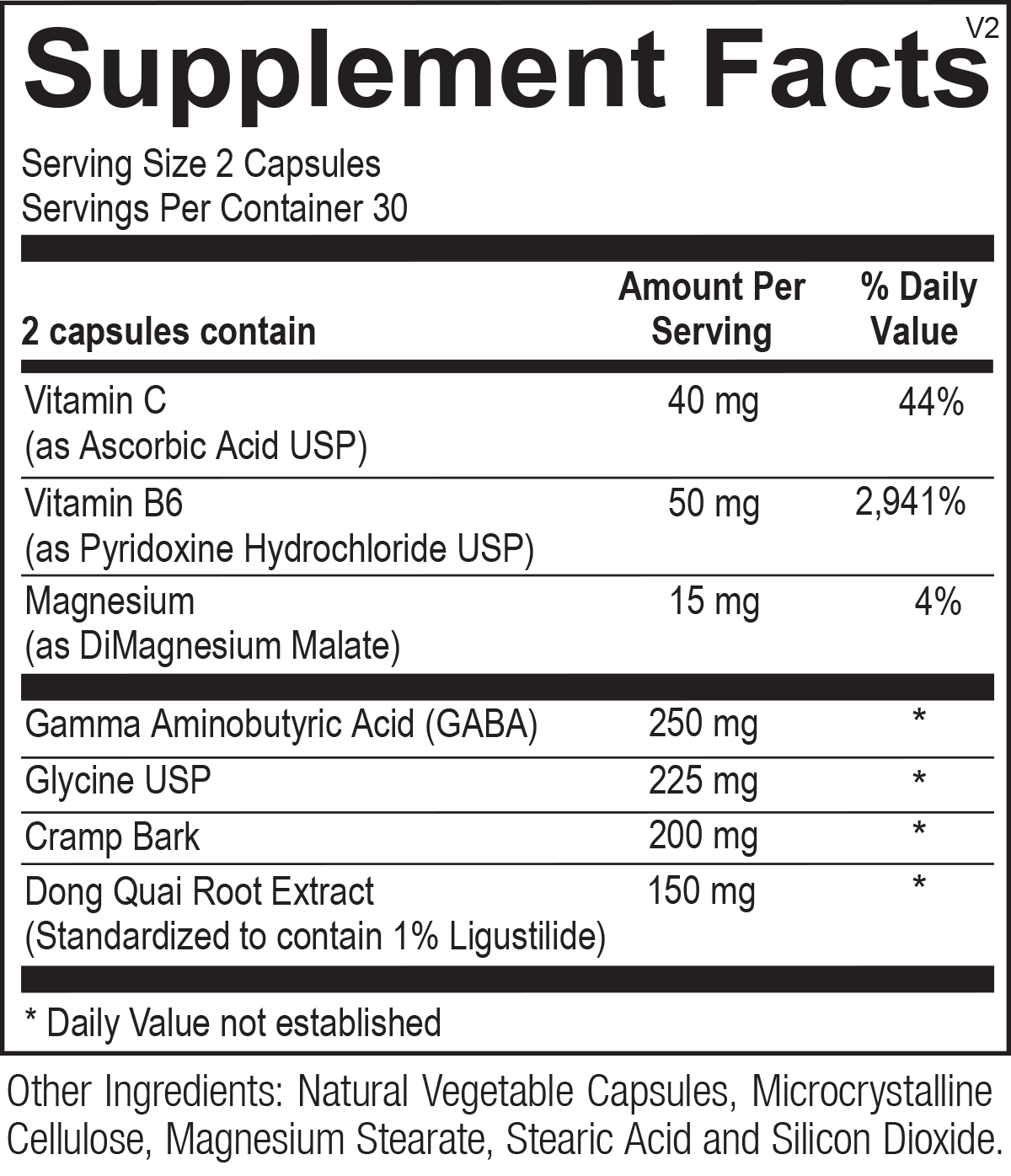
GABAnol is a synergistic combination of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine and established traditional botanicals, which serves as a quick response supplement for muscle relaxation. This unique blend of botanicals, amino acids, vitamins and minerals also work to quickly support muscular discomfort.
Suggested Use:
1-2 capsules three times per day or as recommended by your health care professional.
INGREDIENT BENEFITS
GABA
GABA itself is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain and regulates other neurotransmissions to prevent overstimulation.
Glycine
Glycine is one of three amino acids needed for the synthesis of creatine, which supplies energy to nerve and muscle cells. Elevated amounts of glycine are found in the muscles, skin and other connective tissues. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which works much like GABA.
Cramp Bark
Cramp bark powder has long been used to alleviate smooth muscle discomfort. Studies have confirmed that cramp bark promotes a relaxant effect.
Dong Quai
A perennial botanical native to China and Japan, Dong quai is effective at easing post-exercise muscle soreness, and has long been used medicinally for smooth muscle tension.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is required to convert glutamic acid to GABA in the body. Vitamin B6 is also a cofactor in many cellular biochemical reactions, including the release of glucose from glycogen and that of amino acid metabolism, including transamination, deamination and decarboxylation.
Magnesium
Magnesium, the fourth most abundant mineral in the body, participates in about 300-350 enzymatic reactions in nearly all tissues. Deficiency is common and results from poor dietary intake, poor absorption and excessive losses through urine, stool and perspiration. The mineral is very important for regulating the influx of calcium into the muscle cells. When magnesium is depleted, calcium can remain in the muscle cell area longer, causing muscles to cramp.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.